Instructional Design Simulations

Title and Organization
Simulations for New Instructional Designers: ID Process, Client Interaction, Content Analysis. Sponsored by BYU Online and BYU IP&T Department for the Graduate-Level Instructional Design Introductory Course
Date
October 2022 – February 2023
Problem
Students in an introductory instructional design course needed an overview of the instructional design process and experience making decisions when interacting with clients and creating content analyses. The designs needed to be authentic and relatable but allow students to make mistakes in a safe situation
My Role
Simulations – Lead Designer
Course – Assistant Designer
Solution to the Problem
- Planning – I planned each simulation using Simulation Development Planning worksheets and branching scenario designs in Twine. One design was built in Smart Builder by a developer and I developed the other two in H5P.
- ID Process Overview: This simulation is situated in an authentic context of a corporate ID developing a short course for a company. In small groups, students complete small portions of the process, followed by a class discussion and individual reflection.
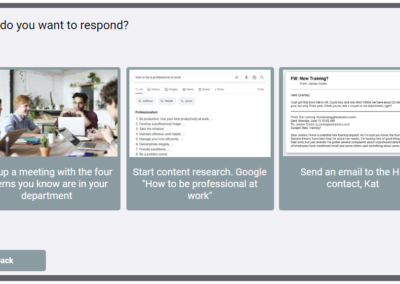
- Client Interaction: Students are in a contract designer position where they interact and make decisions with a client. Students face five of the most common trouble spots with instructional design clients. The simulation is completed in small groups, followed by a class discussion and an individual reflection.
- Content Analysis: Through two separate scenarios, students are tasked with deciding on the type, format, and content-gathering methods for a procedural analysis and a topic analysis. Again, students complete the simulation in small groups, followed by a class discussion and an individual reflection.
Challenges
- Planning and implementing a branching scenario, especially in H5P, was difficult at first but in combination with Twine, it’s much easier to build and edit in testing phases.
- These are complex topics with high levels of ambiguity in many instances, so creating adequate immediate feedback was sometimes difficult.
- For the Instructional Design Process overview, trying to briefly explain the process of designing instruction without oversimplifying elements and without focusing on one specific design method or model was challenging.
Design Strategies
- Extensive research on the development and implementation of simulations for Higher Education including recommendations for fidelity level and reflection/debriefing.
- Situated the simulation within the larger course, so each simulation connects with content and activities before and after to support learning.
- Viewed the content of the course as a whole and then broke down elements of the process into simpler parts that included an authentic skill needed to complete the element. For example, students watched a very brief prototyping video and then added the problem and suggestions for changes to a prototype report document.
- Students reflect on the experience and how their perceptions have changed and what strategies they will apply in future design situations.
Results
Students feel they have a better understanding of these key moments and somewhat complex topics. They feel better equipped with strategies for managing the ID process, interacting with clients and developing content analyses.
ID Process Overview Design Gallery
ID Process Planning with Post-Its
I added many ID process parts to post-its which made it easy to reorder and organize and group them
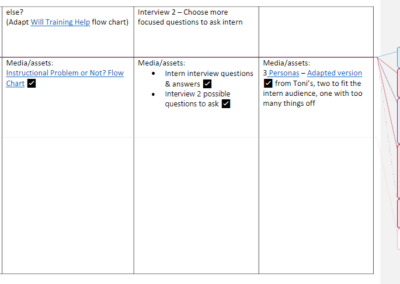
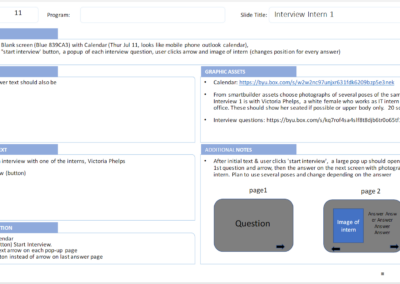
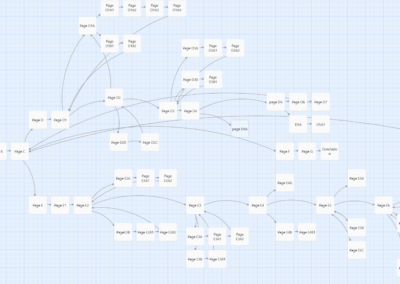
ID Process Storyboard
Storyboard example showing what user sees/hears, how they interact, graphic assets and layout notes for the developer
Client Interaction Design Gallery
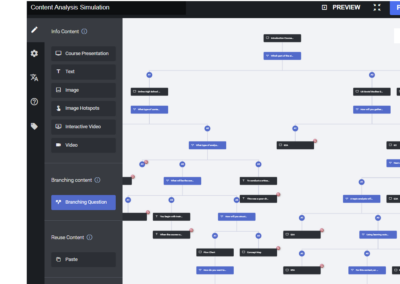
Client Interaction Development Planning
This planning worksheet was crucial to making initial decisions
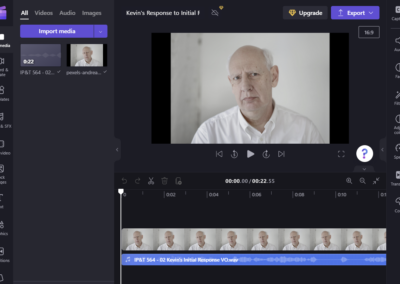
Audio Snippets Created in Clip Champ
I used Clipchamp plus recordings from the media team to create short audio clips